



The American healthcare industry has been impacted by Information Technology (IT) digitization, making healthcare more accessible and affordable. This will not be successful unless patient engagement is encouraged to advance innovative digitized healthcare. Healthcare providers must work in partnership with the patients to ensure that the target is achieved. Digitally engaging patients does not rely on face-to-face meetings, but rather will allow for remote diagnoses and treatment recommendations. An Infosys study (2013) indicates that a high number of patients favor electronically sharing personal health information with their physicians and feel confident that their personal medical data will not be compromised. Many patients share personal medical information online and on mobile devices, and even use their mobile apps to communicate with physicians. Patient engagement occurs when they understand the benefits of services offered by the healthcare systems through marketing campaigns and promotional offers. Patients will be empowered once they are educated on the programs that allow them to manage their own healthcare, including patients who are not technologically savvy and are reluctant to use digitized healthcare systems.
©2015, IJMHS, All Right Reserved
PATIENT ENGAGEMENT IN DIGITAL HEALTHCARE
The impact of Information Technology (IT) on the American healthcare industry has resulted in the digitization of the healthcare system. This has helped it to become safer, more affordable and accessible. This digitized sector has provided the chance to practice theory and obtain in-depth knowledge about the patient (Ritu Agarwal, 2010). With technological advances, digital healthcare quality has been improved, and also has helped to reduce costs by overcoming many challenges, such as providing medical care in remote locations. However, patient engagement must be promoted to advance the success of innovative healthcare digitization.
To achieve digital healthcare success, patient satisfaction must be the primary goal, which can only be achieved when they are fully engaged with the system. To achieve this, healthcare providers must work in partnership with the patients to ensure that the target is achieved (Healthcare, 2014). Patients must take ownership and responsibility for change in their behavior which will improve health outcomes and lower costs. Patient engagement in the healthcare means continuously creating positive experiences that make stronger, more rewarding patient/healthcare relationships that can be provided by technology companies.
Patient-Centric approach
Engaging patients does not mean physically meeting with them and having face-to-face interactive sessions. Rather, the digitized healthcare system will provide an outstanding
experience for the patients by allowing for remote diagnosis and treatment by storing patient data and health insurance plans that can be accessed remotely (Bala, 2014).
Outcome Oriented
Patient engagement can also be achieved by guaranteeing outcome delivery to avoid problems created by physical interactions of healthcare providers and patients when outcomes are delayed or do not live up to patient needs or expectations.
Infosys (2013) conducted a study between the digitally aware consumers and the businesses that serve them. Some findings for the U.S. portion of the survey showed that:
• 92 percent of patients favor physicians having their personal health information electronically
• 80 percent of patients have confidence that their physicians protect personal medical data
• 98 percent comfortably share health data personally with physicians
• 77 percent share personal health data online
• 66 percent of patients share health data on mobile devices
• Approximately 80% will use mobile apps to communicate with their physicians
Patient engagement can be achieved when the services offered by the healthcare systems revolve around the benefits achieved by consumers. This approach can be exercised when customers are acquired and retained on the basis of micro-segmentation, and are reached through
marketing campaigns and promotional offers. Consumer consultation in this system also helps in not only guiding the patients to the right plan, but also having them select a plan that is helpful in the future. Patients must be clearly informed about the plan in order to maintain transparency and quality. Personalized correspondence over the digital network will help resolve issues and fulfill patient needs. The patients will feel more empowered when they are educated on the programs that are committed to managing their own healthcare. This will help patients who are not technologically savvy and often feel reluctant to use these healthcare systems.
Since patients can be connected by social media to voice their opinions, it is important for the digital healthcare system to delight their patients through an effective customer response structure (Dolgin, 2013), such as noted
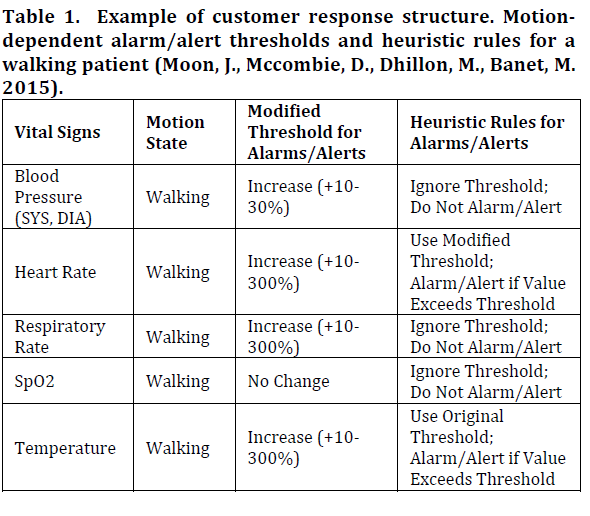
Patients will value the importance of the digital healthcare system if they view it as compatible, simple to use, sees other using it, and are enthusiastic about trying it. The medical journey of the patient must be properly administered to improve customer engagement (Berger, 2014).
1. Bala, V. (2014). Consumer Engagement. Retrieved from http://www.infosyspublicservices.com/insights/Documents/consumer-engagement.pdf
2. Berger, S. (2014, March 26). The Patient Information Journey. Retrieved from blue latitude: http://bluelatitude.net/the-patient-information-journey/
3. Dolgin, G. (2013, November). Consumer Engagement is the Future of Healthcare. Retrieved from Endeavour partners: http://endeavourpartners.net/consumer-engagement-is-the-future-of-healthcare/
4. Healthcare, D. (2014). Customers. Digital Healthcare. Retrieved from http://www.digital-healthcare.co.uk/customers.aspx
5. Infosys (2013). Engaging with Digital Consumers. Retrieved from http://www.infosyspublicservices.com/industries/healthcare/white-papers/Documents/engaging-digital-healthcare-consumers.pdf)
6. Moon, J., Mccombie, D., Dhillon, M., Banet, M. (2015). Body-worn pulse oximeter. W
a. 2010148205 A. Patents. Retrieved from http://www.google.com/patents/WO2010148205A1?cl=en
7. Ritu Agarwal, G. (2010). The Digital Transformation of Healthcare: Current Status and the Road Ahead. Information System research, 796 – 809.
How to cite this article: TEHRANI, Majid Nik. Patient Engagement in Digital Healthcare. Innovative Journal of Medical and Health Science, [S.l.], v. 5, n. 2, p. 37-38, mar. 2015. ISSN 2277-4939.
Available at: <http://innovativejournal.in/ijmhs/index.php/ijmhs/article/view/50>. Date accessed: 09 Apr. 2015. doi:10.15520/ijmhs.2015.vol5.iss2.50.37-38.
Error: Contact form not found.